Jun Zhang
“In a world where multiple stakeholders provide information, there are millions of things that interact in real-time. The system of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is very important because it aims to utilize these assets in a sustainable way.[1]”
Background
Digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT) have a tremendous impact on our world. According to CISCO [2], during 2008, the number of things connected to the Internet exceeded the number of people on earth. Large-scale cloud infrastructure and other network-enabled devices require cooperation and interaction, such as sensors, smart fixed and mobile platforms (such as smartphones, tablets, and home gateways) to create value in many areas of smart cities. This digital environment creates a database of information explosions. This is the key driving force for making the living community smarter. In a smart city, the added value is to save costs and improve efficiency by making objects smarter, thereby achieving long-term economic growth and sustainable development [3]. To realize the vision of sustainable smart city applications, it is necessary to enhance the Internet of Things (IoT) technology in new ways, so that things and objects become more reliable, more autonomous, and more intelligent. Nowadays, The IoT technology and related big data applications are clearly on a penetrative path across the systems and domains of smart sustainable cities.
Figure 1: What is internet of things(IoT)? (Eric Le Cunff, 2019)
What are the current IoT applications?
Sensor technology is one of the core technologies of the Internet of Things. A variety of IoT architectures are essentially designed to provide appropriate infrastructure for the operation of the IoT ecosystem to respond to the application of smart sustainable cities. 1.Weather system: Weather and water systems can utilize some sensors to provide suitable information like temperature, rain, wind speed, and pressure and can contribute to enhance the efficiency of the smart cities. 2.Smart parking lots and traffic system: By enabling smart parking, arrival and departure of various vehicles can be tracked for different parking lots distributed in the city. The data of smart parking lots can bring advantages for both vehicle owners and merchants daily lives in a smart city. By using the data with analytical computation, citizens and government planning departments can benefit a lot.3.Smart home: The energy efficiency of households can be dramatically improved through smart home applications, including smart lightings, smart HVAC systems, and so on. A large number of smart-home applications use sensor networks. 4. Surveillance systems: Security should still be a big concern in smart cities. Surveillance systems can prevent citizens from more crimes and emergent accidents. [4]
What are the future IoT applications?
In the future, the IoT general architecture provides the media to be everywhere incorporating transparently and seamlessly as shown in Figure 2. 1. Responsive city: The governance of the responsive city encourages and enforces transparent and timely responses from the operational to the strategic level. It builds on advances in citizen engagement, cyber-civil infrastructure and computing methods that focus on the interpretation of sensor data, modelling uncertainty, probabilities and identifying unknown dependencies. [5] 2. Smart Grid: The utilization of the IoT can furnish intelligent management of energy distribution and consumption in heterogeneous circumstances. The IoT nodes have some abilities such as sensing and networking which raise the possibility of optimal scheduling of energy suppliers. This management can also be extended to emergency conditions. [6] 3. To be continued: more and more potentials are being developed and even more ideas are being generated to build smarter cities with IoT technology.
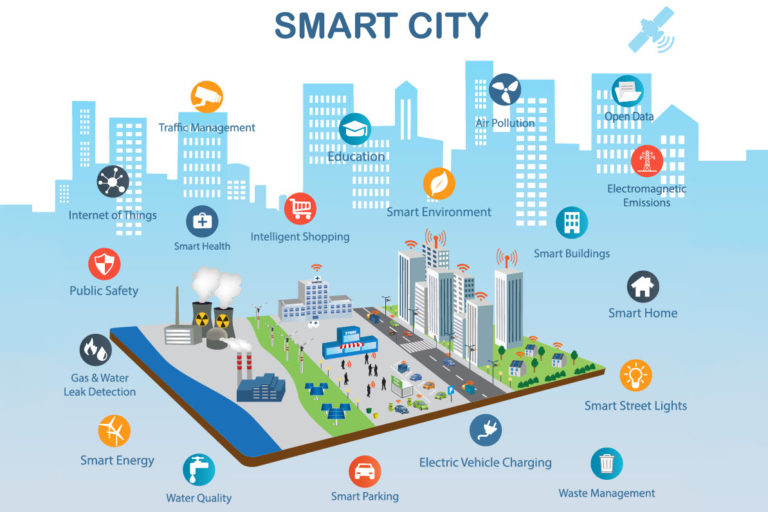
Figure 2: Potentials of IoT (Epko van Nisselrooij, 2019)
What are the Challenges?
IoT-based smart cities have to face challenges as well. The side effect and technical bottleneck will be with the development of IoT technology all the time. 1. Privacy: like all other concerns regarding big data and surveillance systems, the system can be subjected to several attacks. The collected data will expose the city’s vulnerabilities. Multi-tenancy of this system can also bring out the security issues and cause the leakage of data. 2. Big data: the development of big data technology is fast but not able to store and analyze so much information from IoT. Different stakeholders should have enough incentives to participate in the defined scenarios and data collection. 3. Reliability: Some reliability problems have appeared in the system based on the Internet of Things. For example, due to the mobility of the vehicle, the communication with the vehicle is not reliable enough. In addition, the existence of many smart devices will bring some reliability challenges in terms of reliability. [7]
References
Kyriazis, Dimosthenis, et al. “Sustainable smart city IoT applications: Heat and electricity management & Eco-conscious cruise control for public transportation.” 2013 IEEE 14th International Symposium on” A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks”(WoWMoM). IEEE, 2013.
CISCO, The Internet of Things, Infographic, available online at http://blogs.cisco.com/news/the-internet-of-things-infographic, 2011
http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/us/en, 2012
A. Botta, W. de Donato, V. Persico, and A. Pescapé, “Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: a survey”, Future Gener. Comput. Syst., vol. 56, pp. 684–700, 2016.
Bibri, Simon Elias. “The IoT for smart sustainable cities of the future: An analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability.” Sustainable cities and society 38 (2018): 230-253.
https://fcl.ethz.ch/research/responsive-cities.html
Yun, Miao, and Bu Yuxin. “Research on the architecture and key technology of Internet of Things (IoT) applied on smart grid.” 2010 International Conference on Advances in Energy Engineering. IEEE, 2010.
Latre, Steven, et al. “City of things: An integrated and multi-technology testbed for IoT smart city experiments.” 2016 IEEE international smart cities conference (ISC2). IEEE, 2016.