Behailu Bereded
“What are the potential Challenges to transform Agriculture and the Way forward, towards the achievement of SDGs in Developing Countries?”
Background
Many of our challenges can be greatly addressed by sustainable food and agriculture as there is a prime connection between people and the planet, and this helps to achieve multiple sustainable development Goals (SDGs) (FAO, 2018). Sustaining the agriculture sector is likely a pillar for achieving the SDGs 2030 especially for developing countries as their economy largely depends on this sector. Although this sector is mainly focused on Goal 2 of SDGs (World with Zero Hunger), it is the joint footstep which holds all the SDGs together directly and indirectly. Attaining SDGs in this sector to maximize agricultural productivity without any negative impact on the environment and sustaining the resource is to use the optimal amount of water, fertilizer, chemical, and seeds as well. To achieve the 2030 UN SDGs of zero hunger, an urgent transformation of the current Agri-food system through digital technologies are part of the solution (FAO, 2019).
Food and Agriculture organization proposes the following five key principles (Figure 1) for guiding the strategic development of new approaches and the transition to sustainability in food and Agriculture.
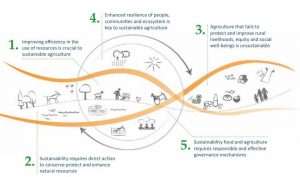
Figure 1: The Five Principles of sustainable food and Agriculture (FAO, 2014)
Why Digital Technologies for Agriculture?
Digital technologies have the potential to revolutionize agriculture by helping farmers work in an efficient, effective and sustainable way. They provide the agricultural industry with tools and information to make more informed decisions & improve productivity, and enable improved development of agricultural products, providing peace of mind for consumers and increased value for farmers (http://agriculture.vic.gov.au/). Data-driven insights can improve decision making and practices that could help in increasing the environmental quality & sustainability. Digital technologies inclusive of infrastructure and connectivity through mobile subscription & internet access in rural areas transform agriculture by expanding and managing access to information on capital & resources through precision tools in a more efficient way
Beyond farming, they play a key role in making rural communities more attractive, smart and sustainable, reducing problems with regard to the remoteness and improving access to services (https://ec.europa.eu).
Challenges and possible solution
The main longstanding challenge in developing countries like ‘Africa’ is strongly tied to low productivity stemmed from lack of access to technology besides other constraints like shortage of access to market & credit, corruption, poor governance, and agricultural policy implementation. Lack of infrastructure & resources, education, affordability of the technology and ICT systems are other additional potential challenges.
The aforementioned challenges can be tackled by developing concrete legal policies and designing a working framework that could support the farming system with the required & necessary marketing setup, making continuous conversation along with farming supporters, conducting effective farmer capacity building, and using knowledge-agriculture with skilled farmers that are capable of using digital technologies, which are potentially critical for achieving the looked-for goals aimed at SDGs.
The Way forward
Of course, tremendous effort is required from all stakeholders to transform the agriculture into a digital system; it is possible if all stands together. To my view, the government and policymakers must first be transparent, impartial and free from any corruption so that a good atmosphere is created. Secondly, influence and encouraging the farmers through awareness about the application and its use through media and other information dissemination options. Thirdly, adopt technologies from the developed countries and design them with appropriate low-cost local materials to make it affordable to the small scale farmers. Fourthly, form a strong linkage between research institutions and higher education to exchange knowledge and skills. Fifthly, improvements in the ICT policies and expansion of technologies like mobile phones and internet accessibility will have a great impact on rural growth and sustainable business. Lastly, investing in the new generation is very crucial in technology perspectives.
In this blog, I tried to mention the issues, challenges and the way forward options to transform the agriculture with digital technologies and its strong link in enhancing the SDGs for developing countries.
“The Future Is Now”
References
Salami, A., Kamara, A. B., & Brixiova, Z, (2017), Smallholder agriculture in East Africa: Trends, constraints, and opportunities, African Development Bank Tunis, Tunisia.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2018), Transforming food and agriculture to achieve the SDGs. 20 interconnected actions to guide decision‐makers.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2019), digital technologies in agriculture and rural areas briefing paper, Rome, Italy.
https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/food-farming-fisheries/farming/documents/factsheet-agri-digital-transformation_en.pdf, (Accessed Date, April 20, 2020)
http://agriculture.vic.gov.au/agriculture/digital-agriculture/about (Accessed Date, April 20, 2020)
Media Attributions
- The Five Principles of sustainable food and Agriculture